Explore the working principles and features of wired and wireless crane remote controls to help you make an informed choice.
What is a Crane Remote Control?
Cranes are ubiquitous in our lives, including Overhead Cranes (also known as EOT cranes), tower cranes, truck-mounted cranes, electric hoists, and gantry cranes. All these cranes rely on a common device – the Crane Remote Control. Let’s explore what a Crane Remote Control is.
As the name suggests, a Crane Remote Control is a device designed specifically to control crane movements and operations. It allows for more convenient, precise, and safe operation of cranes.
Common Functions of a Crane Remote Control:
- Motion Control: It allows the operator to control crane movements in various directions (up, down, forward, backward, left, right).
- Speed Control: Different controllers can be configured for single-speed, dual-speed, or variable speed control, allowing operators to adjust the crane’s speed as needed.
- Safety Features: Controllers are equipped with emergency stop buttons, authorization start devices, and overload protection to ensure safe crane operation.

Common Types of Crane Remote Controls:
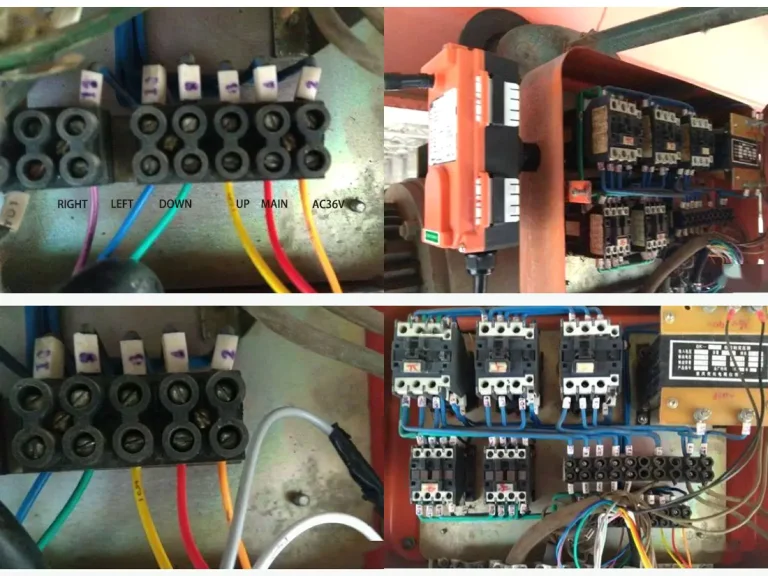
- Wired Crane Remote Control: Connected to the crane via cables, requiring the operator to follow the crane and operate from a fixed position.
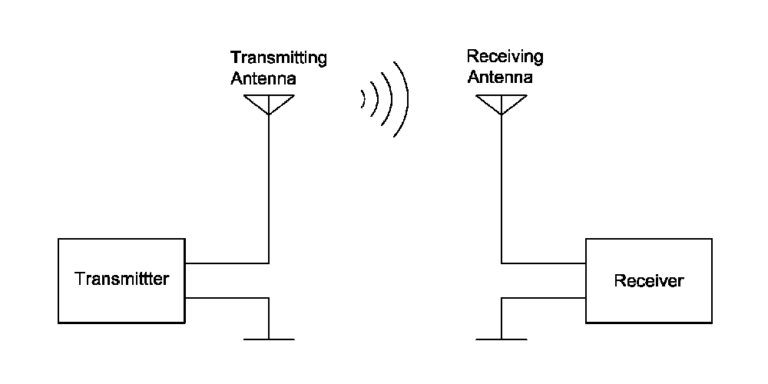
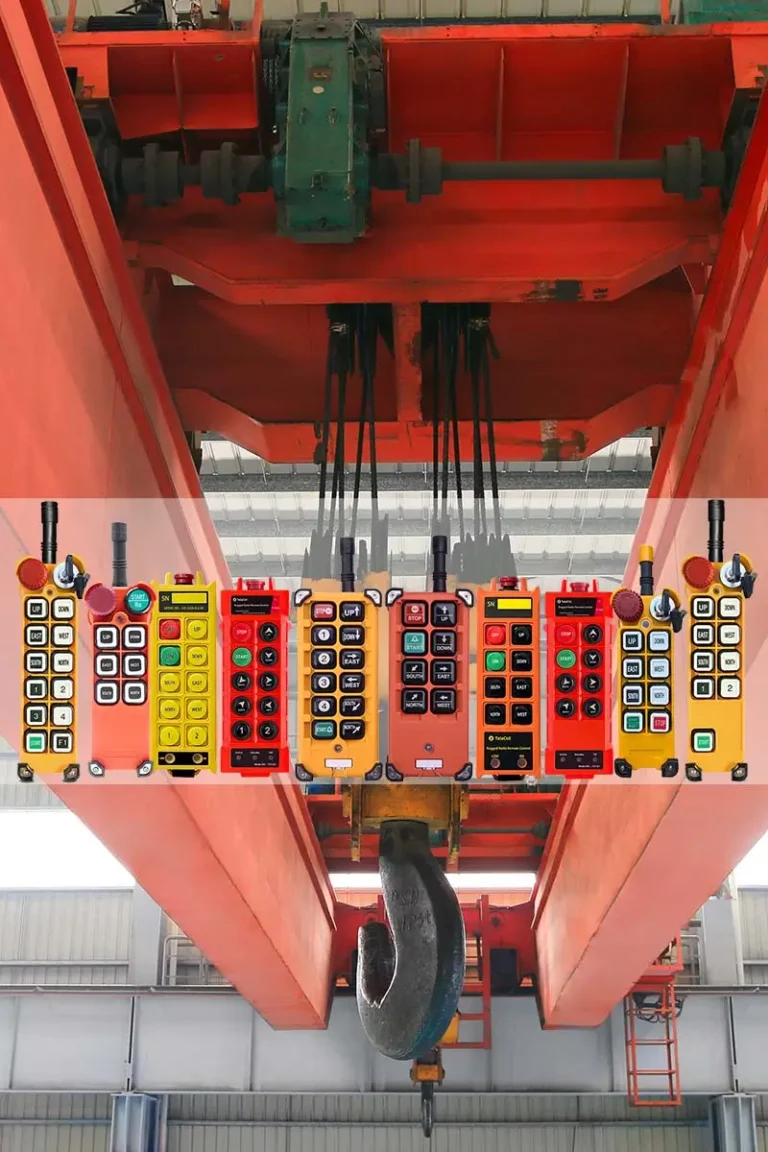
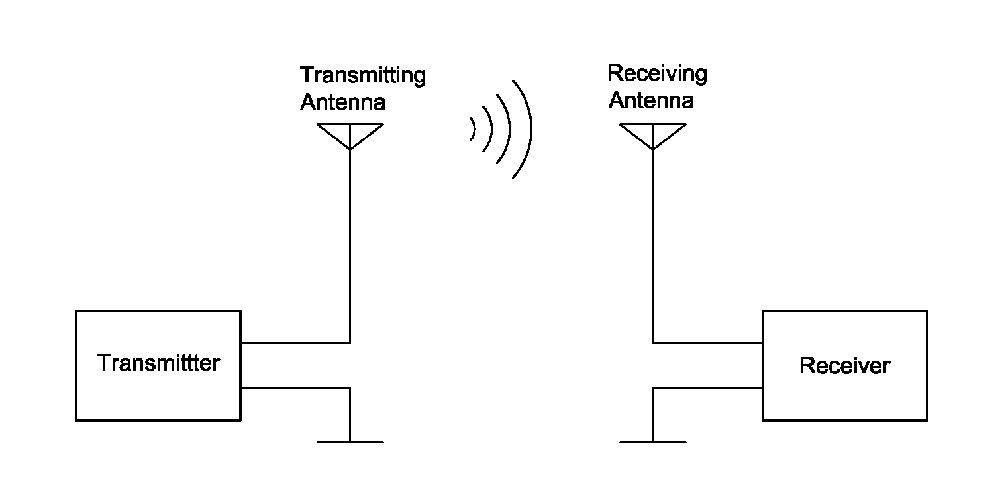
- Wireless Crane Remote Control: Wireless design using radio waves for signal transmission, allowing the operator to control from a convenient and safe location.
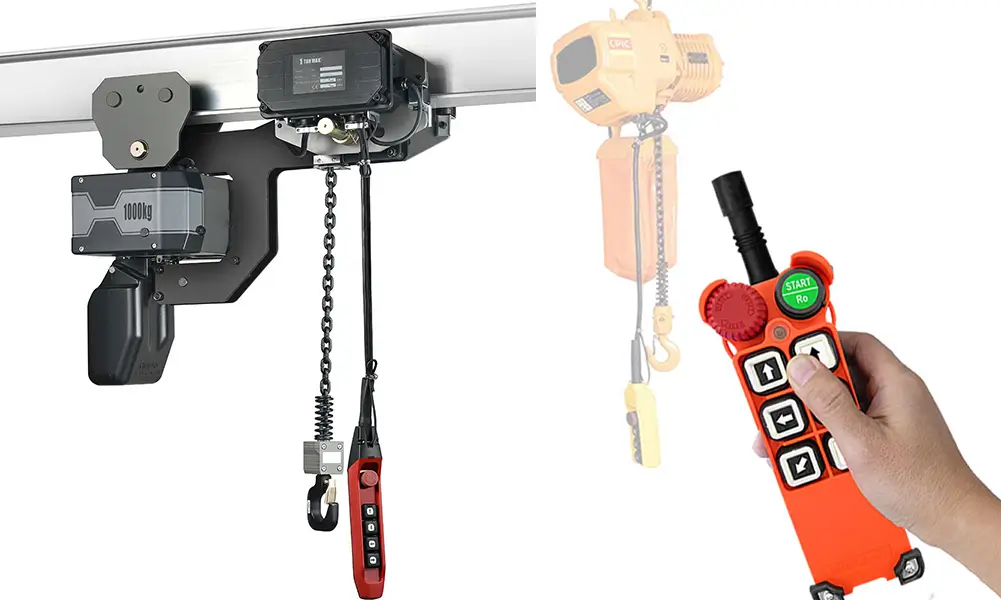

You can click on “Radio Remote Control” to learn more about Wireless Crane Remote Control products;
You can also click on “Crane Remote Control” to learn more about the applications of Radio Remote Control in the Crane and Hoist industry.
Differences Between Wired and Wireless Crane Remote Controls
Working Principle:
- Wired: Uses physical cables to connect and transmit control signals.
- Wireless: Uses radio frequency technology to transmit control signals via radio waves.
Installation and Maintenance:
- Wired: More complex installation requiring wiring and securing. Regular inspections and replacements are necessary to prevent electrical hazards due to cable aging.
- Wireless: Easy installation without wiring, powered by batteries, eliminating electrical hazards. Regular battery checks and replacements are required.
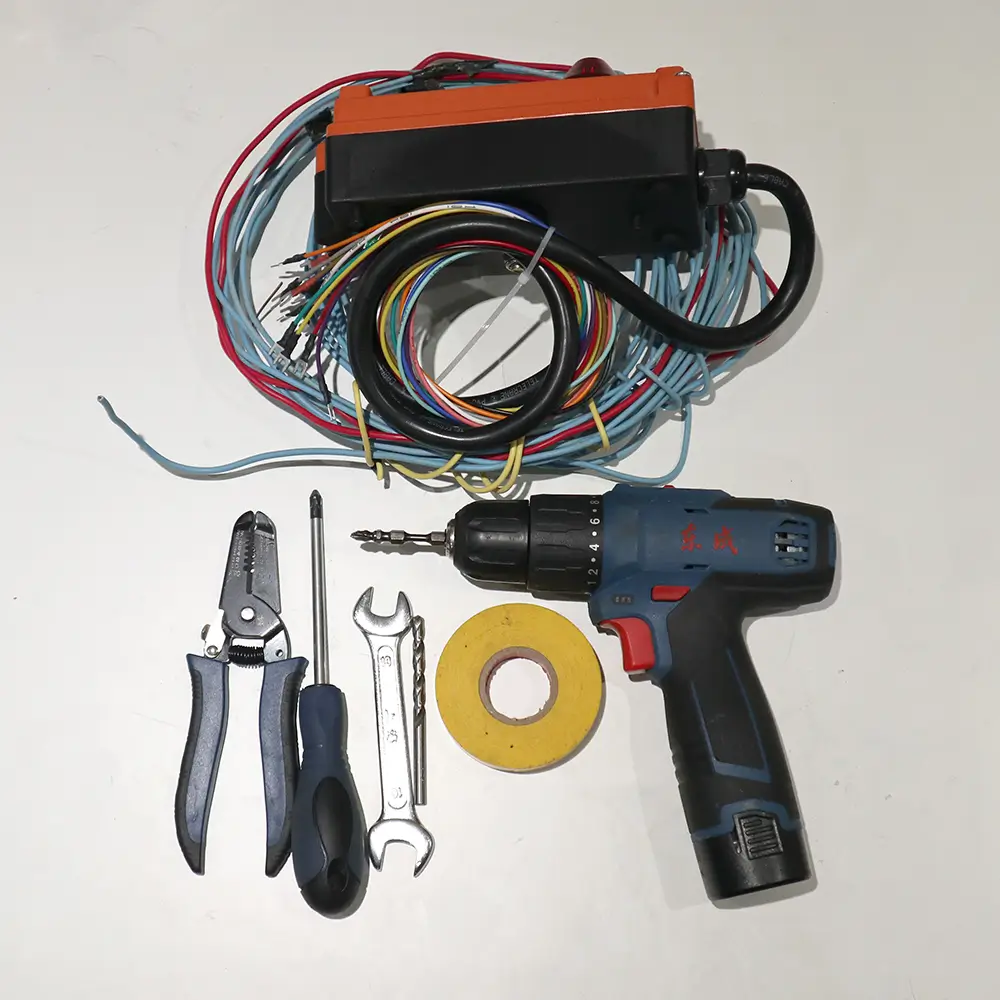

Click “Comprehensive Guide to Installing and Wiring Industrial Radio Remote Controls” to learn more about the installation and maintenance of Wireless Crane Remote Controls.
Environmental Adaptability:
- Wired: Suitable for equipment control within a fixed work area, but less convenient and being increasingly replaced by wireless options.
- Wireless: Broader adaptability and not obstructed by barriers, increasingly replacing wired controllers in many fields.
Operational Flexibility:
- Wired: Operator must follow the crane, limited by cable length.
- Wireless: Operator can freely choose the best position with an unobstructed view to operate safely.
Safety:
- Wired: Signal transmission is interference-free, but cable wear and falling objects pose risks.
- Wireless: Avoids operating in dangerous environments (toxic, high heat, light pollution, obstructed views) and reduces risks of electrical shocks and tripping from cable wear. TeleCtrl’s Wireless Crane Remote Control uses advanced frequency hopping and narrowband communication technology to minimize signal interference.

Work Efficiency:
- Wired: Requires following the crane and may need an additional operator, reducing efficiency.
- Wireless: Eliminates the need for extra operators and allows control from multiple positions, reducing unnecessary movements and improving efficiency.
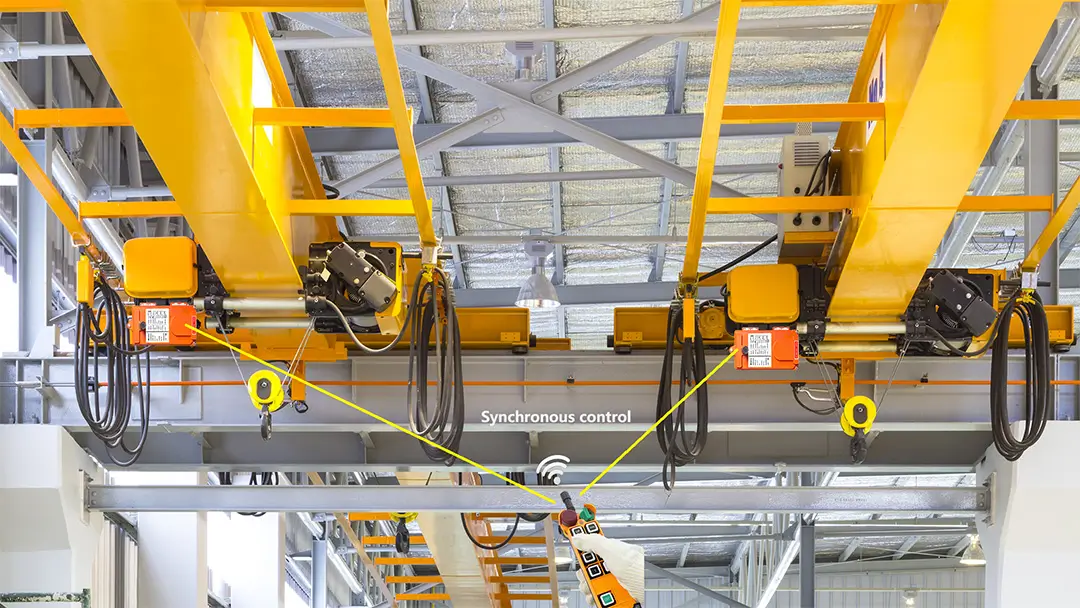
Equipment Synchronization:
- Wired: Difficult to achieve synchronization between multiple devices due to wired connections.
- Wireless: Easy to set up synchronization, allowing one controller to control multiple cranes or multiple controllers to control a single crane.

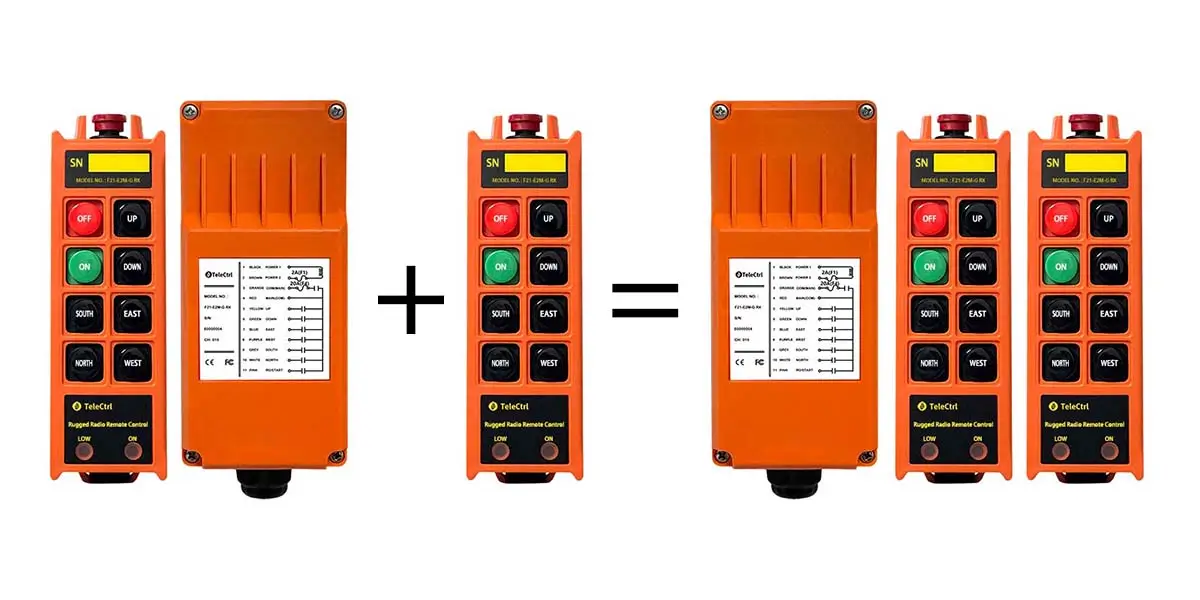
Emergency Backup:
- Wired: Repair requires professional assistance, causing potential production delays.
- Wireless: Additional transmitters can be used as backups, allowing immediate replacement if one fails.

Cost Considerations:
- Wired: Lower installation and maintenance costs, but higher costs due to additional operators and reduced efficiency.
- Wireless: Higher initial cost for wireless configuration, but lower maintenance and operation costs.
User Experience:
- Wired: Traditional operation, familiar to operators but less flexible and convenient.
- Wireless: Similar to traditional wired buttons, easy for operators to use without additional training, and more flexible and convenient.
Customization:
- Wired: Typically provided by crane manufacturers, difficult to customize.
- Wireless: Can be customized with specific button layouts and functions as needed.

If you are interested in custom remote controls, click “Custom Radio Remote Control” for more information.
The above comparison highlights the differences between Wired and Wireless Crane Remote Controls. If you are considering upgrading your crane controller, contact the experts at TeleCtrl Industrial Remote Control. As one of the largest manufacturers of Wireless Crane Remote Controls in China and globally, TeleCtrl has extensive experience and technical expertise, producing and customizing various industrial remote controls for many renowned companies worldwide with an excellent reputation.