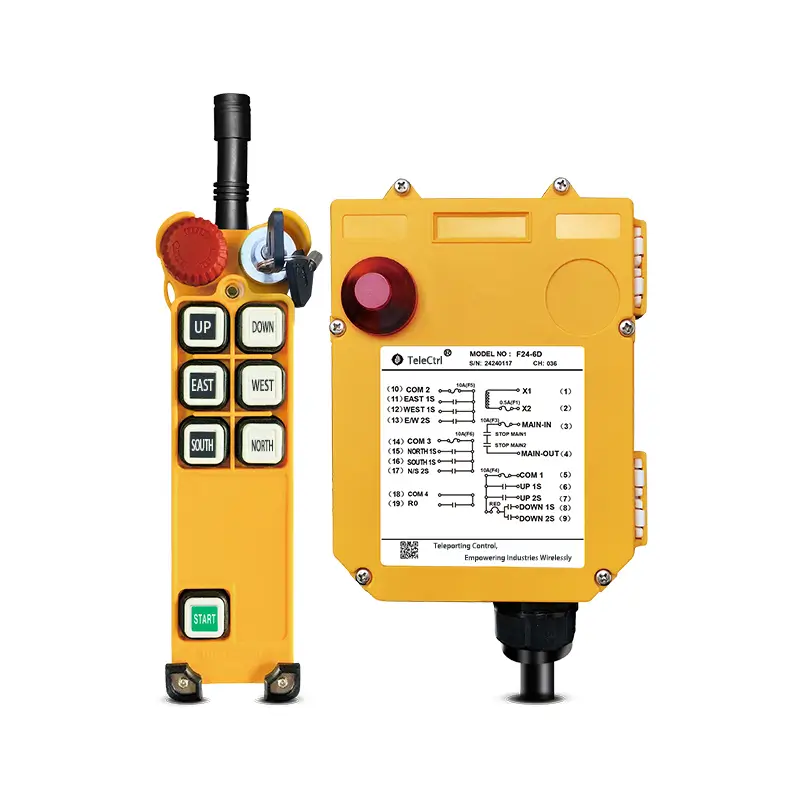
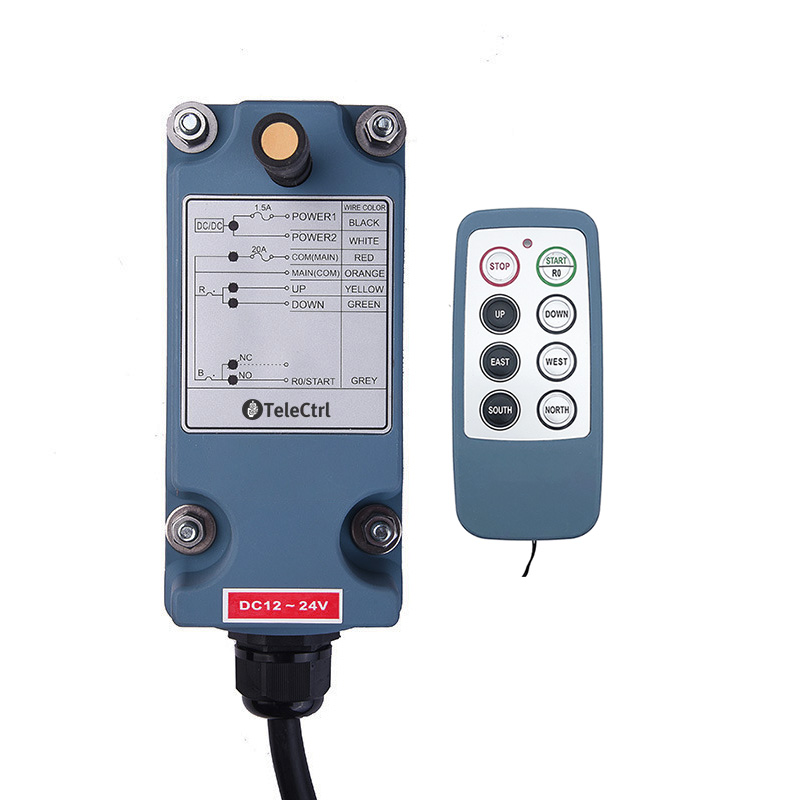
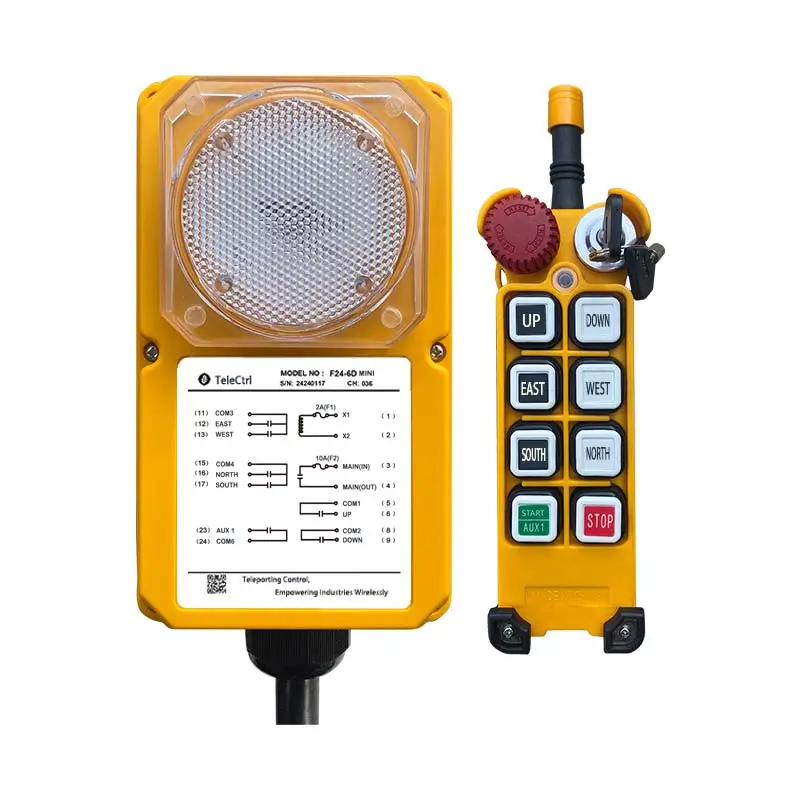
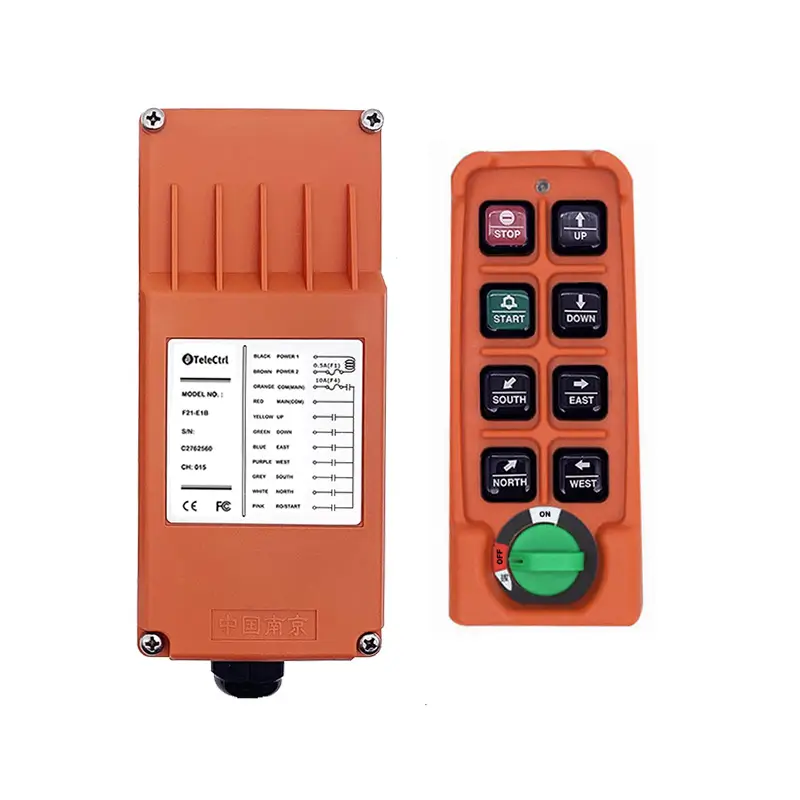
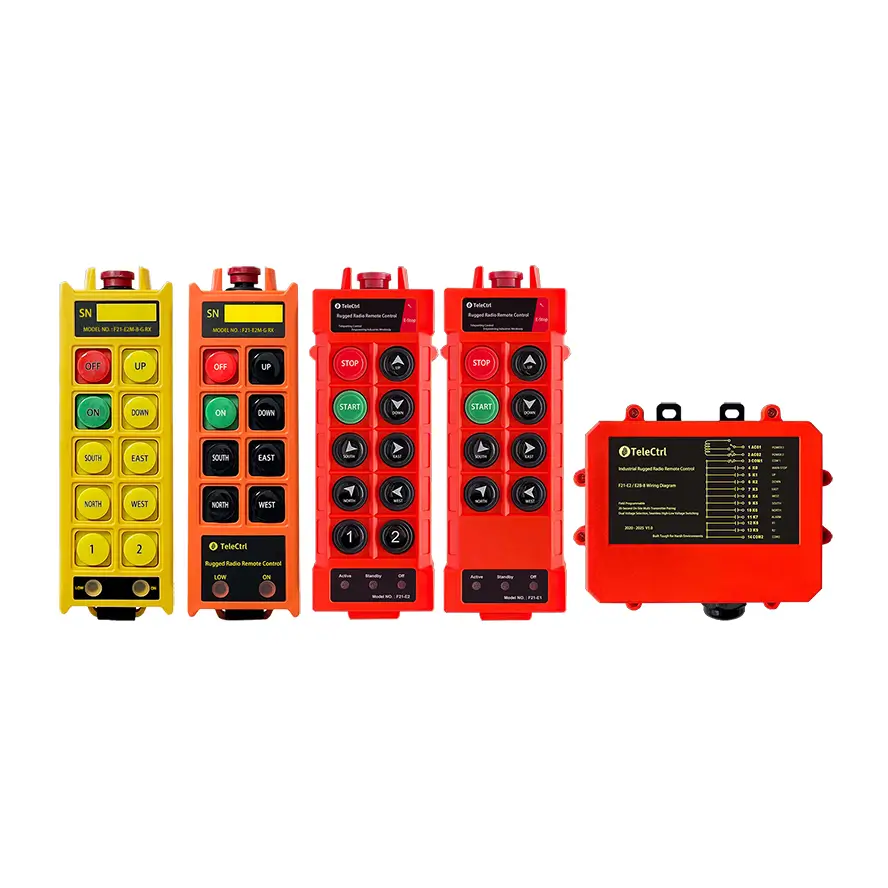
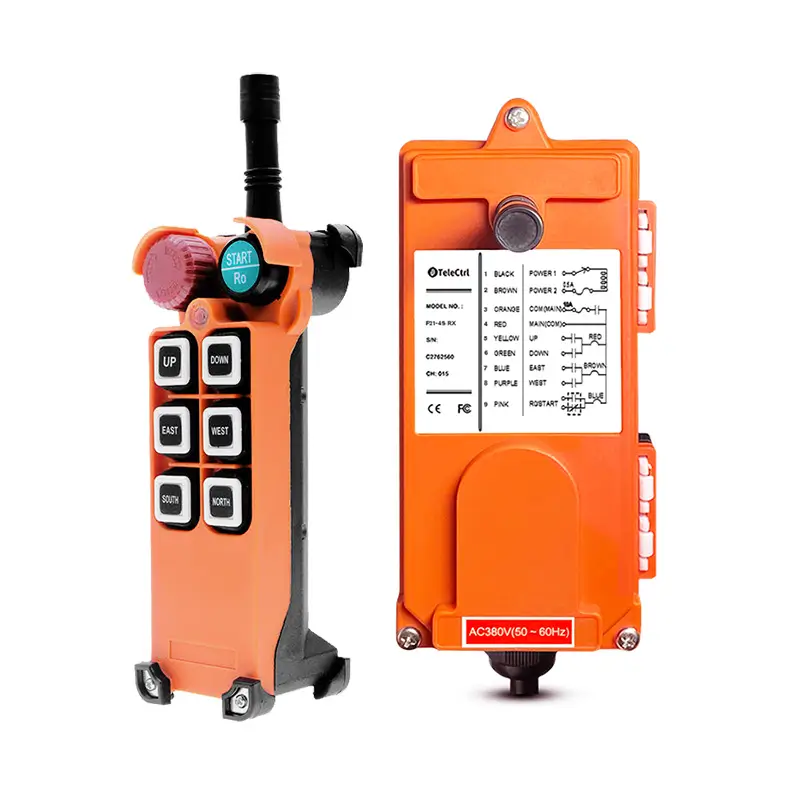
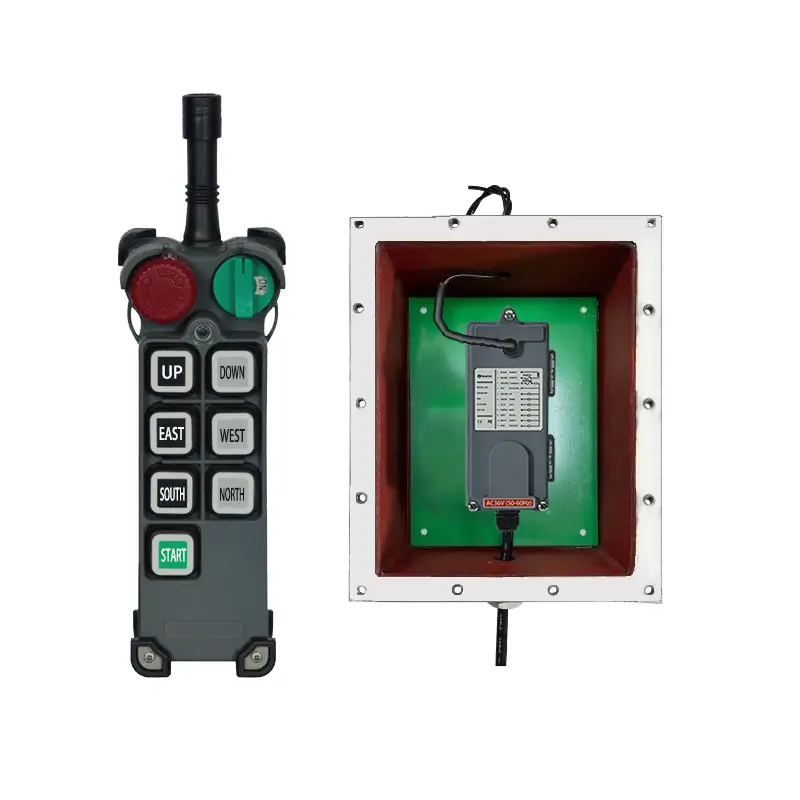
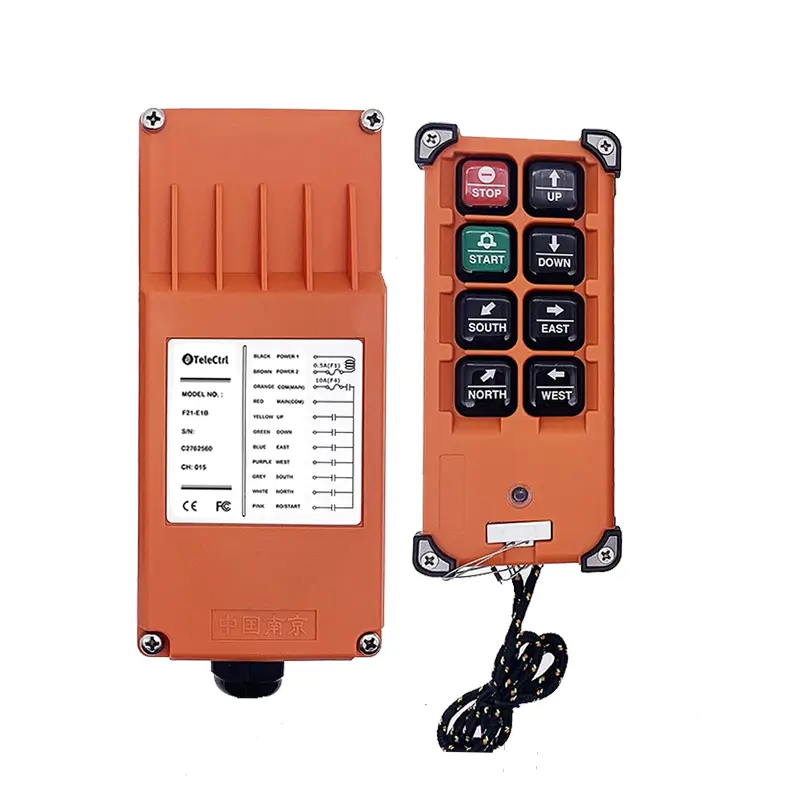
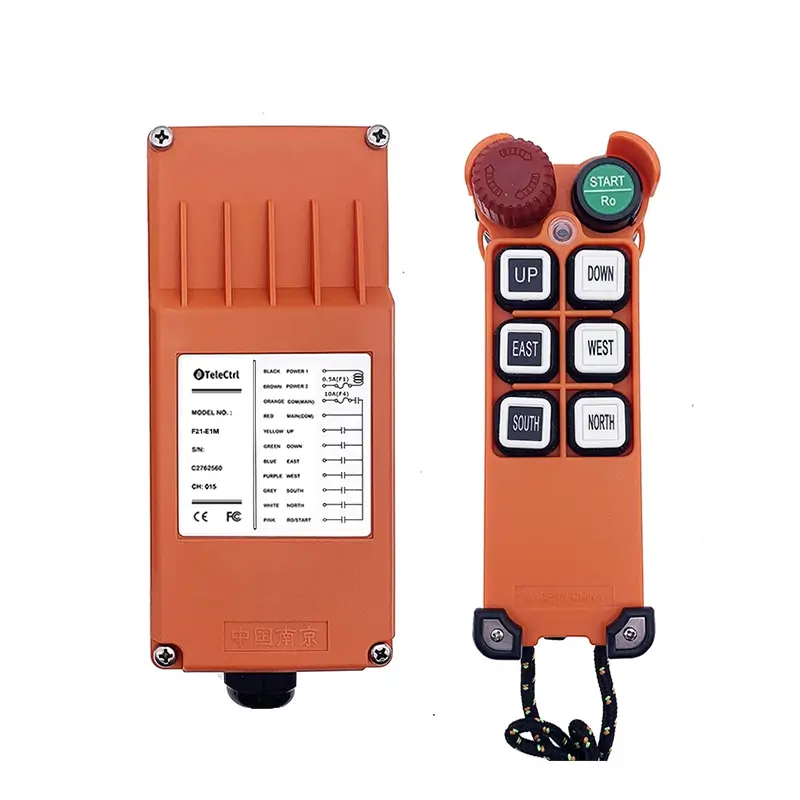
Tower Crane Wireless Remote Control
Learn about the features and advantages of using wireless remote controls for tower cranes, providing guidance for purchasing tower crane remote controls.
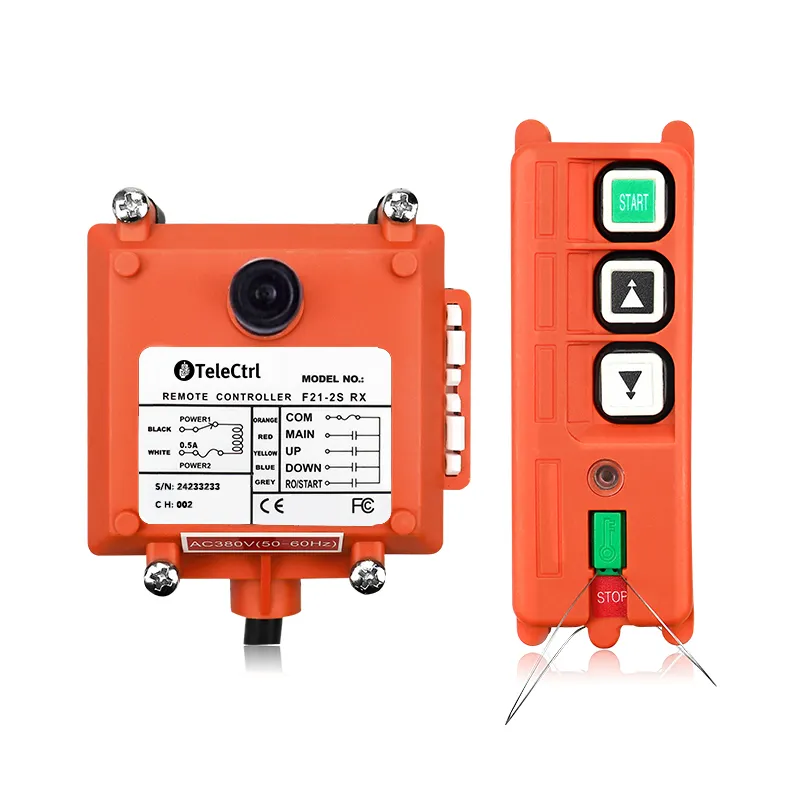
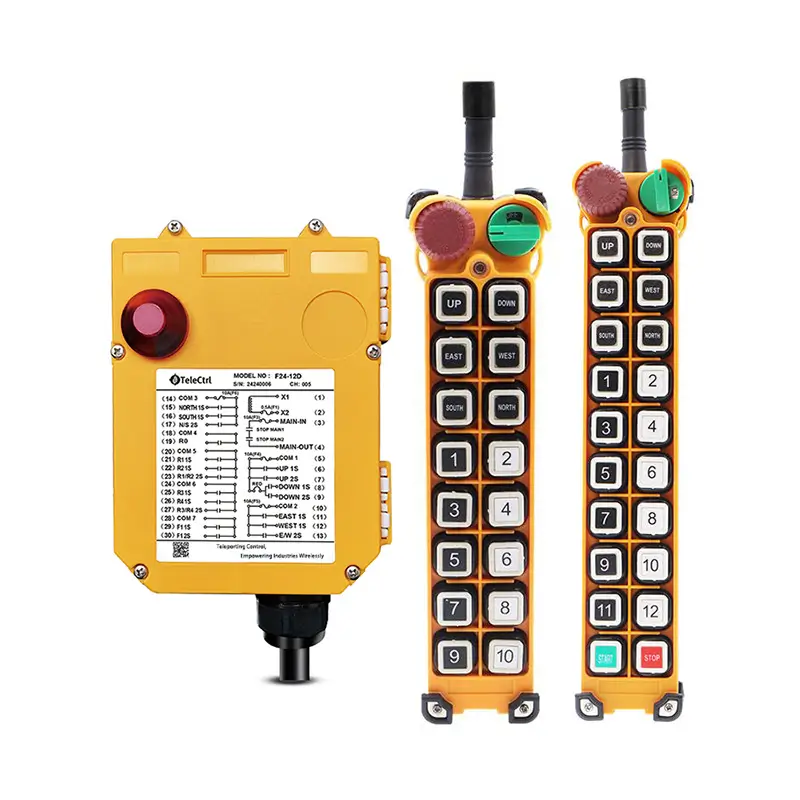
What is a Tower Crane Remote Control?
Tower cranes are commonly used in the construction industry to lift and move heavy materials on job sites. Traditionally, these cranes are controlled from a cab located at the top of the tower, where the operator controls lifting, rotating, and moving operations. With the advancement of remote control technology, remote controls specifically designed for tower cranes have become increasingly popular. These remote controls allow operators to control the crane from a safe distance, offering a safer, easier, and more precise way to manage the crane’s movements, thus improving efficiency and reducing operator risk.
Common Control Methods and Features for Tower Cranes
- Cab Control: The most traditional control method where the operator sits in a cab at the top of the tower crane, using joysticks and buttons to control the crane’s movements. This method requires the operator to work at great heights, demanding high physical and mental endurance.
- Wired Controllers: These are connected to ground-level controllers via cables, allowing the operator to control the machine from the ground. However, the operating range is limited by the cable length, and visibility can be obstructed, making the operation less safe.
- Wireless Controllers: These use radio waves to transmit control signals, allowing operators to choose safe and suitable positions with optimal visibility for operating the machine. This significantly enhances operational flexibility and safety, reducing the need for dedicated personnel in the cab. Wireless control has become the most popular method.
- Remote Control Systems: More advanced systems that allow operators to control the crane via computers or dedicated control panels from a location far from the construction site, typically over the internet. These systems often include video monitoring and various sensors, providing safer and more precise control but are usually expensive and used in specialized applications requiring high security and precision.
Common Issues in Tower Crane Control
- Communication Failures: Whether using wired or wireless control methods, communication failures can occur. In wired systems, cable wear or poor connections can lead to signal loss, while in wireless systems, excessive control distance or signal interference can cause signal loss or interruptions.
- Operator Errors: Due to the complexity of tower crane controls, inexperienced operators may make mistakes, leading to incorrect movements that can cause serious accidents.
- Weather Conditions: Adverse weather conditions such as strong winds, thunderstorms, or extreme temperatures can affect tower crane operations. For example, strong winds can cause crane swaying, and thunderstorms pose a risk to operators in high cabs.
- Load Issues: Overloading can damage equipment or cause collapses, while uneven loads can unbalance the crane arm, affecting operational stability and increasing the risk of dropped loads, posing significant danger.
- Emergency Situations and Safety Devices: Regardless of the control method, emergency safety devices such as emergency stop buttons and limit switches should be in place.
Advantages of Using Wireless Tower Crane Remote Controls
- Enhanced Safety: Wireless remote controls allow operators to operate the crane from a safe distance, avoiding dangers like strong winds, high temperatures, and other potential hazards.
- Increased Operational Flexibility: Operators can freely choose the best vantage points to control the crane, no longer restricted by traditional control rooms. This flexibility allows for more effective responses to varying site conditions and demands.
- Improved Precision: Operators can position themselves closer to the work area, providing better control and accuracy, especially when lifting precision components or operating in confined spaces. This reduces the likelihood of errors and accidents.
- Reduced Personnel Requirements: Traditional cab control often requires dedicated personnel, with limited ability to rotate operators due to the high-altitude working environment. Wireless control reduces the need for auxiliary operators, and in less demanding environments, the main operator can manage other tasks simultaneously.
- Increased Efficiency: With better visibility and no need to move between the control room and ground, wireless controls reduce operational delays and enhance work efficiency.
- Convenient Emergency Operations: In emergencies, operators can quickly move to a safe location while still controlling the crane, such as by swiftly pressing the emergency stop button to prevent accidents.
Learn more about Tower Crane Wireless Remote Control.
You may have other questions about Tower Crane Wireless Remote Control. Continue to explore more about its frequently asked questions.